# VMess
VMess protocol is originated from and utilised in V2ray, and it is similar with Shadowsocks which is designed for obfuscating internet traffic to cheat Deep packet inspection (opens new window) of GFW. VMess is the primary protocol used to communicate between server and client.
In this section, we provided an example of VMess configuration, which is a set of the basic configuration files for the server and client. This type of configuration is the most straightforward configuration that V2Ray can help you pass through internet censorship.
The JSON configuration file of V2Ray uses inbound (incoming) and outbound (outgoing) structures. This structure reflects the traffic flow direction of the packet and making V2Ray powerfully and functionality without being confusing and clear. To put it bluntly, we can think of V2Ray as a box with entries and exits (i.e. inbound and outbound). We put the packet into the box through a gate, and then the box has some mechanisms (this mechanism is called routing, which will be discussed in detail in another chapter) to decide which outbound the packet will spit out from. In this way, if V2Ray is the client, inbound receives the data from the browser and is sent outbound (usually sent to the V2Ray server). V2Ray acts as the server and inbound receives the data from the V2Ray client, which is sent by outbound (usually a target site like Google that you want to visit).
# Preparation before configuration
In fact, you don't have to prepare anything as long as you have a text editor to modify the configuration. However, there are still some friendly reminder, since many beginners wrote the wrong syntax or format in their JSON configurations. That is common due to beginners are not familiar with these command line tools, and may use Windows Notepad as their primary JSON editor. We do not recommend Windows Notepad due to its poor support in encoding and line ending options.
Instead, VSCode is a useful tool for writing JSON, and it also supports reformatting, which is powerful for beginners. Moreover, there are plenty of other text editors, such as Sublime Text, Atom, Notepad++, etc. They are all versatile and easy to use, and you may Google them for details. These software have features like code highlighting, folding, reformatting, so again, they are highly recommended. If you don't want to install any software, there are also some online JSON editors you can find online, and the syntax will be checked automatically.
The below image is a comparison between Notepad and Sublime Text, for your as a reference to choose the better one.
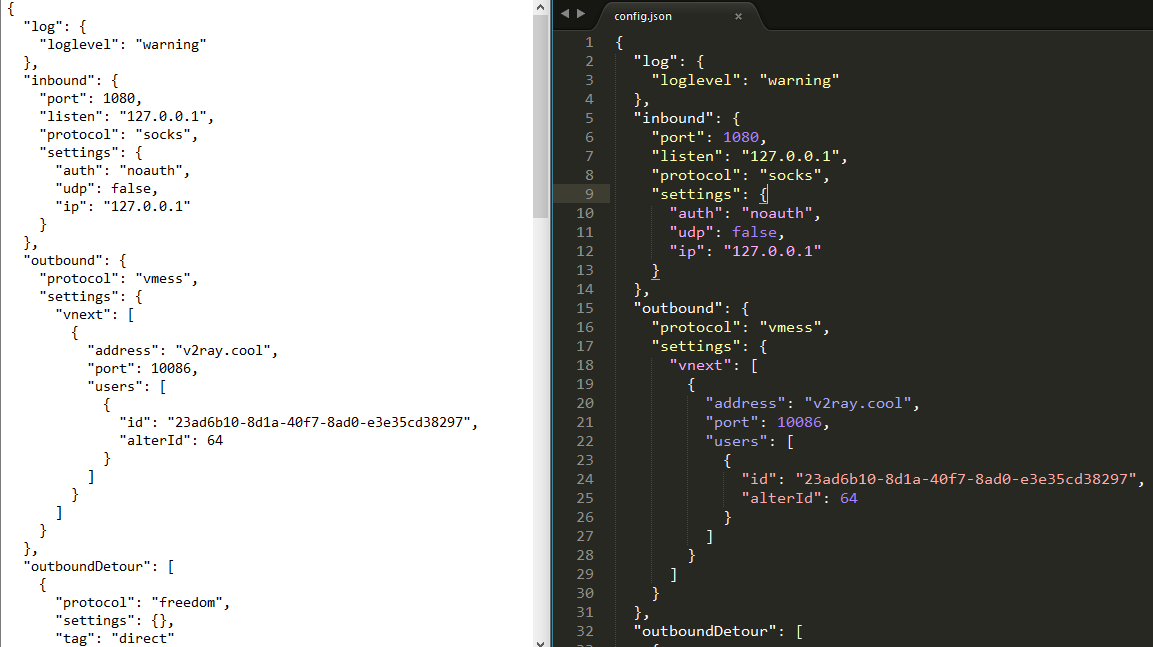
JSON file formatting as another example:
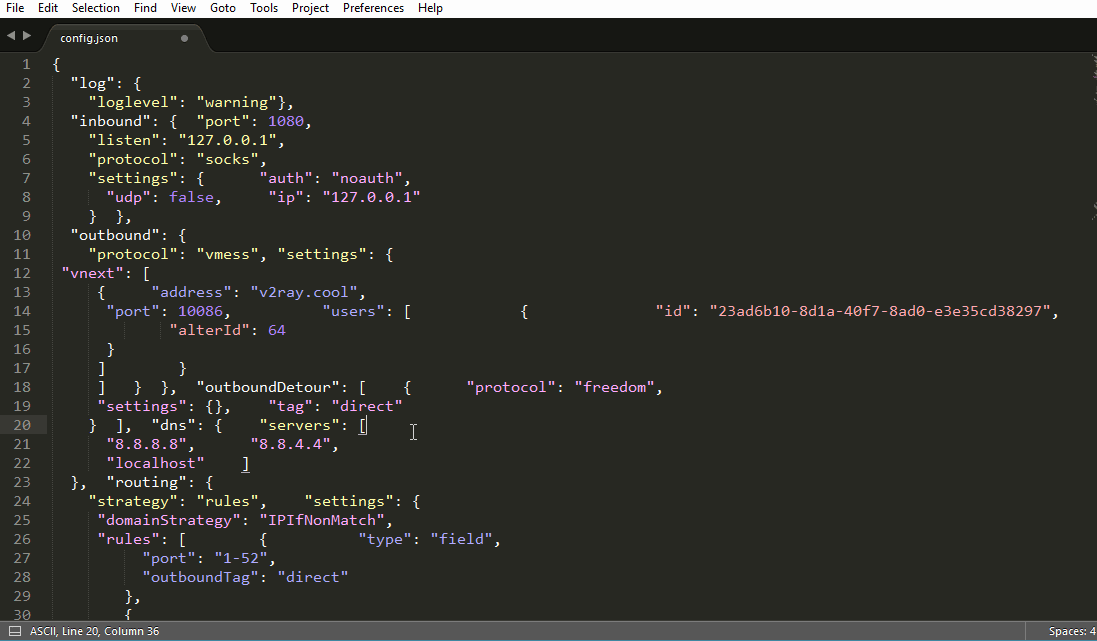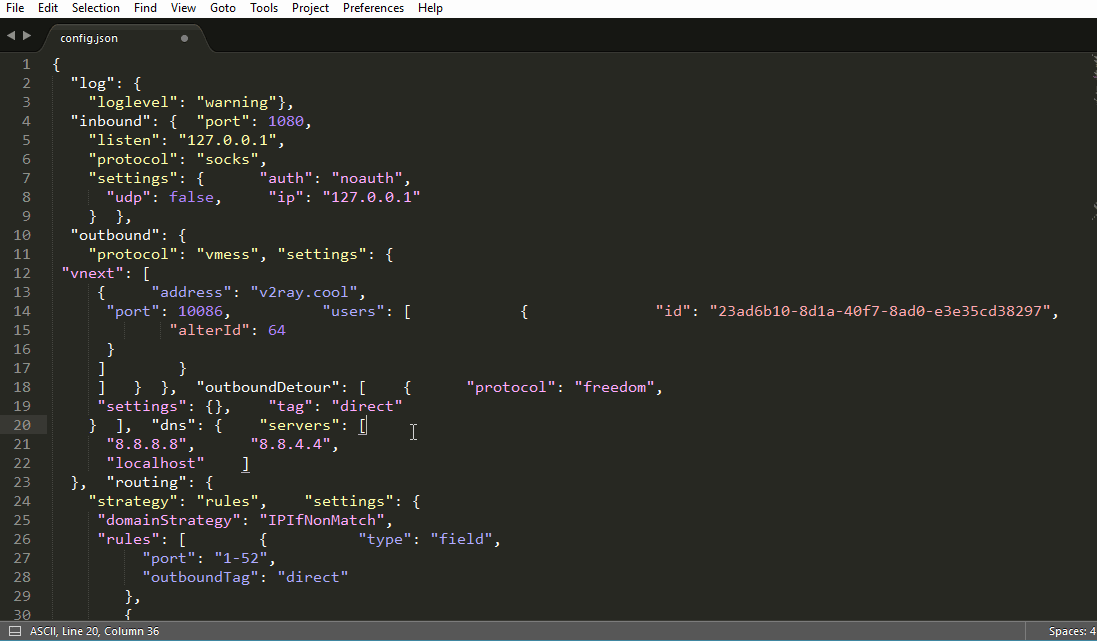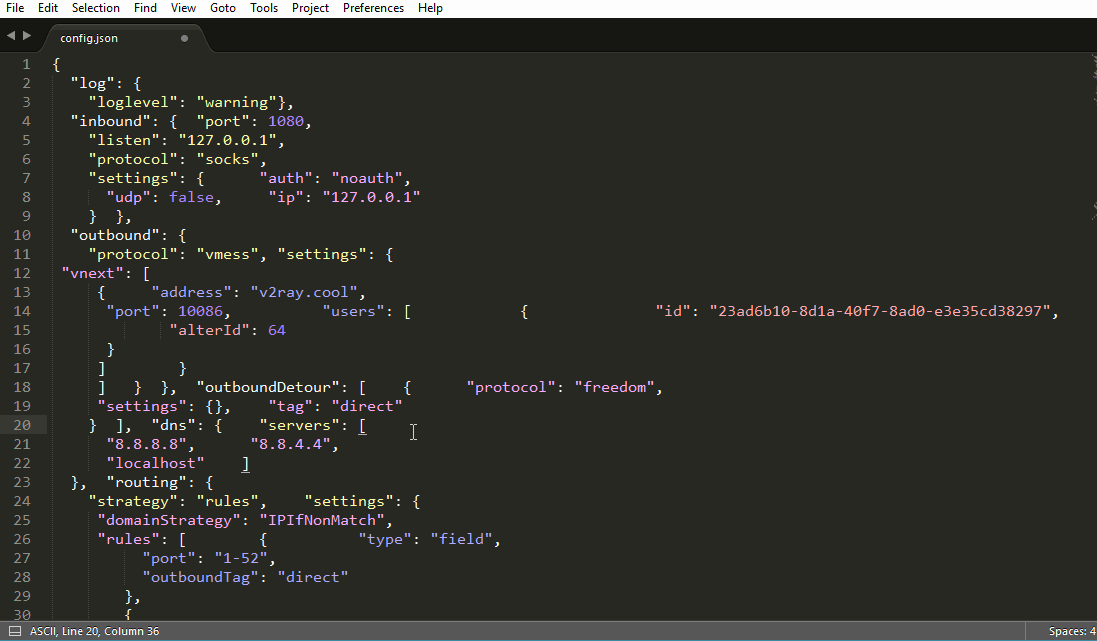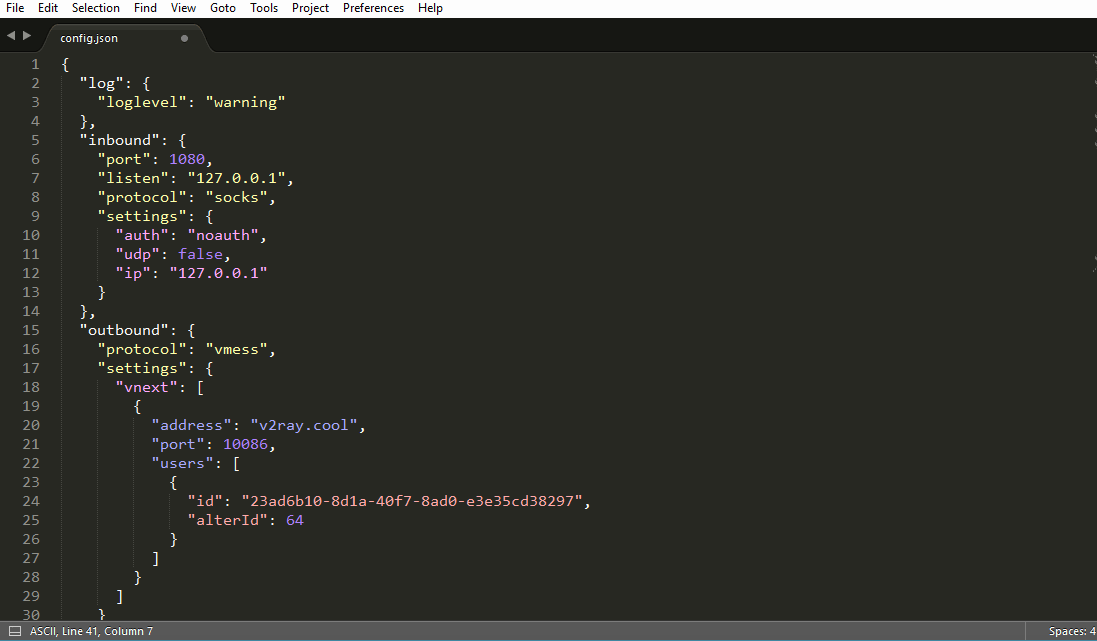
There is a command line tool called jq, by executing the following command, you can check the grammar of configuration file.
$ jq . config.json
Here config.json is the config.json file in the current directory. Pay special attention to the period in the command. You can't ignore it.
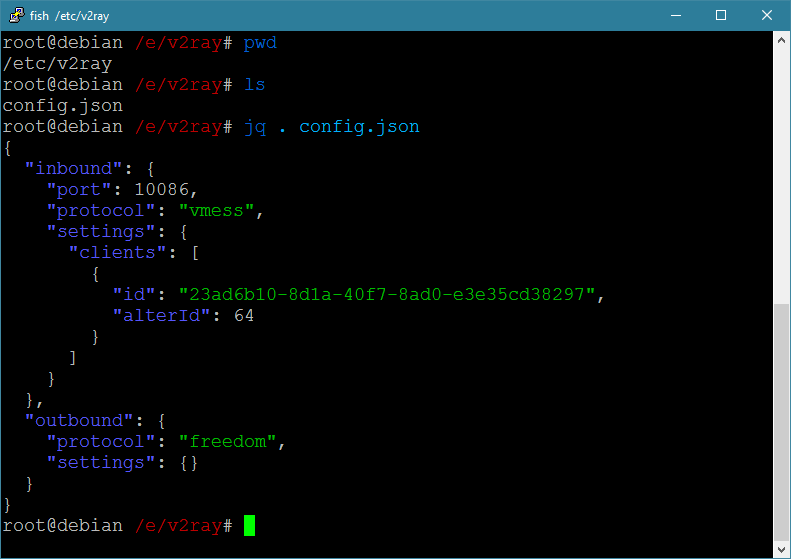 When I delete the comma after "23ad6b10-8d1a-40f7-8ad0-e3e35cd38297":
When I delete the comma after "23ad6b10-8d1a-40f7-8ad0-e3e35cd38297":
Note that, a comment feature has been added since V2Ray v2.11. The configuration file allows // and /**/ comments which is not supported by official JSON format. Therefore it is supposed to be reported as error in some error-checking tools. Don't panic.
However, it is recommended to use the configuration check feature provided by V2Ray (-test option) because you can check for contents other than JSON syntax errors, such as typo vmess as vmes.
$ /usr/bin/v2ray/v2ray -test -config /etc/v2ray/config.json
failed to parse json config: Ext|Tools|Conf|Serial: failed to parse json config > Ext|Tools|Conf: failed to load inbound detour config. > Ext|Tools|Conf: unknown config id: vmss
Main: failed to read config file: /etc/v2ray/config.json > Main|Json: failed to execute v2ctl to convert config file. > exit status 255
If the configuration file is ok, then returned message will be like this:
$ /usr/bin/v2ray/v2ray -test -config /etc/v2ray/config.json
V2Ray v3.15 (die Commanderin) 20180329
An unified platform for anti-censorship.
Configuration OK.
# Configuration Example
We give the example configuration files as below, including server-side and client-side. You need to replace your configuration to the below one, and replace the server IP address/domain to yours; then you can enjoy uncensored internet. Note that, the configuration will not be applied until you restart the V2Ray.
Notice
The authorisation of the VMess protocol is based on time. It must be ensured that the system time between the server and the client is within 90 seconds.
# Client-side Configuration
The following is the client-side configuration, edit the client's config.json file to the following content, and restart V2Ray after the modification is complete to make the modified configuration applied.
{
"inbounds": [
{
"port": 1080, // Listening port
"protocol": "socks", // Incoming protocol is SOCKS 5
"sniffing": {
"enabled": true,
"destOverride": ["http", "tls"]
},
"settings": {
"auth": "noauth" // Authorisation setting of socks protocol. Here, noauth means no authorisation, beacuse in general socks only used in client side, so no need to authorise.
}
}
],
"outbounds": [
{
"protocol": "vmess", // Outcoming protocol
"settings": {
"vnext": [
{
"address": "serveraddr.com", // Server address, yoou need to edit this to your own IP address/domian.
"port": 16823, // Server listenning port.
"users": [
{
"id": "b831381d-6324-4d53-ad4f-8cda48b30811", // UUID, must be as same as server side
"alterId": 64 // AlterID should be as same as server side
}
]
}
]
}
}
]
}
In the configuration, there is an id used for authorization (in this case is b831381d-6324-4d53-ad4f-8cda48b30811), which acts like Shadowsocks' password. VMess user id must be in the same format as UUID. There is no need to know a lot about id or UUID. It is enough to know the following points here:
- The incoming UUID and the corresponded outgoing UUID of VMess protocol must be the same (if you don't understand this sentence well, you can simply understand that the server and client UUID must be the same).
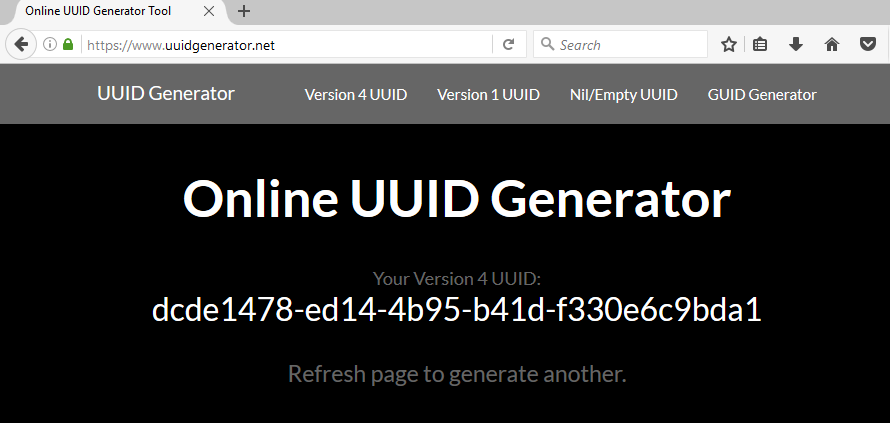
- Since the id uses the UUID format, we can use any UUID generation tool to generate the UUID as the id here. For example, UUID Generator (opens new window). On this website, you can get a UUID as soon as you open or refresh this page, as shown below. Alternatively, it can be generated in Linux using the command
cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/uuid.
# Server-side Configuration
Below is the server configuration. Editing the config.json file in the /etc/v2ray directory of the server to the following JSON. After the modification is complete, restart V2Ray to make the modified configuration applied.
{
"inbounds": [
{
"port": 16823, // Server listening port
"protocol": "vmess", // Major incoming protocol
"settings": {
"clients": [
{
"id": "b831381d-6324-4d53-ad4f-8cda48b30811", // UUID, must to be kept the same between server and client.
"alterId": 64
}
]
}
}
],
"outbounds": [
{
"protocol": "freedom", // Majoy outcoming protocol.
"settings": {}
}
]
}
# What happens?
Here is a simple introduction of how V2Ray working.
Whether the process of V2Ray behaves as a client or a server, the configuration file consists of two parts: inbounds and outbounds. V2Ray does not use the C/S (client/server) architecture of regular proxy software, it can be used either as a server and or a client. In other words, that each V2Ray is a node, inbound is a configuration on how to connect to the previous node, and outbound is a configuration on how to connect to the next node. For the first node, inbound is connected to the browser; for the last node, outbound is connected to the target website. inbounds and outbounds are collections of inbound and outbound, meaning that each V2Ray node can have multiple entries and exits. There are only one entry and exit in this example for ease of explanation and understanding.
# Client-side
Inbounds in the example client configuration, listening port is 1080, that is, V2Ray listens on a port 1080, and the protocol is socks. Assuming that we have set up the browser proxy (SOCKS Host: 127.0.0.1, Port: 1080), then if you visit google.com, the browser will send a packet to the socks protocol to send to the machine to the 1080 port of the local device (127.0.0.1 is your local device, or say localhost). At this time, the packet will be received by V2Ray.
Then let's looking at outbounds, the protocol is VMess, indicating that V2Ray will encrypt the packet by VMess (opens new window) protocol. The packet will be encrypted by the UUID (In this example, UUID is b831381d-6324-4d53-ad4f-8cda48b30811) and then sent the package to remote server address serveraddr.com with port 16823, where the server address and port are. The server address can be either a domain name or an IP address, as long as it is connectable.
In the inbounds configured by the client, there is a "sniffing" field. The V2Ray manual is interpreted as "traffic detection, resetting the requested target according to the specified traffic type". It is not very easy to understand. Say this thing. It is to identify the domain name from the network traffic. This sniffing has two uses:
- Avoid DNS poisoning;
- For IP traffic, the routing rules (mentioned in later chapter) can be applied;
- Identify the BT protocol and intercept or directly connect to BT traffic according to your needs (a section is specifically mentioned later).
If you use the Tor browser, don't turn on sniffing (set the enable option in sniffing section to false), otherwise Tor will not be able to access the Internet.
# Server-side
Then look at the server, the server configuration UUID is b831381d-6324-4d53-ad4f-8cda48b30811, so the V2Ray server will try to decrypt with this key. When receiving the packet sent by the client, if the decryption is successful then check with timestamps. If timestamps are correct between server and clien, the packet will be send to outbound; here the outbound protocol is freedom (means direct connection here), the data packet will be send directly to website such as google.com.
The flow of packets shown as:
{browser} <--(socks)--> {V2Ray client inbound <-> V2Ray client outbound} <--(VMess)--> {V2Ray server inbound <-> V2Ray server outbound} <--(Freedom)--> {Target site}
There is also an alterId parameter in the configuration. This parameter is mainly used to enhance the anti-detection capability. In theory, the larger the alterId, the better, but the larger the memory is (only for the server, the client does not occupy the memory), so setting an intermediate value under the compromise is the best. So how large is the best? In fact, this is a sub-scenario. We have not tested this strictly, but based on experience, it should be appropriate to set the value of alterId between 30 and 100. The size of the alterId is to ensure that the client is less than or equal to the server.
Some people wondered how the data came back after the request was sent. After all, most of the scenes were downloaded. That is actually not a problem. Since the request is sent out via V2Ray, the response data will also be returned via V2Ray. (If you are familiar with IP networks, you probably will say it is not absolute that traffic will be return with the same route. However, we don't need to focus on the network layer, but as an application layer perspective, it can be regarded as the same route.)
# Notes
- In order to give a brief introduction to the way V2Ray works, there are some places where the description of the principle in this section may be not correct. However, it is enough for you to understand the brief principle. The design of VMess protocl is detailed in the VMess Protocol (opens new window) in the developer manual or alternatively you may like to check with the original codes on github.
- The id is in UUID format. Please use software to generate. Don't try to create one yourself, otherwise it will create a wrong format.
- The VMess protocol can set the encryption cipher suite, but the different encryption methods of VMess have no obvious difference for the wall. This section does not give the relevant configuration method (because this is not important, VMess will choose a suitable encryption method by default). The specific configuration can be found in the V2Ray Manual (opens new window). For the performance of different encryption methods, refer to Performance Test.
# Troubleshooting guide
By following instructions above, V2Ray should be deployed successfully. However, there would always be some readers who may be missing some essential points, resulting in wrong configuration after configuration applied. If you have such a problem, you can try to troubleshoot by following the steps below.
# Crash immediately after launch
Possible cause: The client's configuration file is incorrect.
Correction method: Please check the configuration file carefully and modify it correctly.
# Client prompt Socks: unknown Socks version:
Possible cause: The inboud of the client configuration is set to socks and the browser's proxy protocol is set to http.
Correction method: Modify the configuration file to make the protocol of the client's inbound and the protocol set by the browser proxy consistent.
# Client prompt Proxy|HTTP: failed to read http request > malformed HTTP request "\x05\x01\x00"
Possible cause: The inboud configured by the client is set to https and the proxy protocol of the browser is set to socks4 or socks5.
Correction method: Modify the configuration file to make the protocol of the client's inbound and the protocol set by the browser proxy consistent.
# The server executes systemctl status v2ray, the output prompt: Main: failed to read config file...
Possible cause: The server's configuration file is incorrect.
Correction method: Please check the configuration file carefully and correct it.
# Execute cat /var/log/v2ray/error.log or systemctl status v2ray prompt: rejected Proxy|VMess|Encoding: invalid user
Possible cause: The system time or id of the server and the client are inconsistent or the alterId is inconsistent.
Correction method: Please calibrate the system time or modify the id and alterId.
# After the above points are excluded, please check carefully:
1). The port number in the browser's proxy settings is consistent with the client's inbound port;
2). The address of the outbound setting in the client is consistent with the ip of the vps;
3). The address of the outbound setting in the client is consistent with the inbound port of the server;
4). Whether the VPS has enabled the firewall and blocked the connection;
5). Whether the client is installed in a place such as a school or a company. If so, confirm whether these units have a firewall to block the connection;
For 1) to 3), you can check if there is a problem by checking the configuration. For 4) and 5), you need to communicate with the VPS provider and company's network manager.
# If you double-check the above points and rule out the problem, you still can't access the Internet via V2Ray, then you can consider:
1). Read carefully at the tutorial ahead, and follow the tutorial to avoid redeploying V2Ray. Always pay attention to the points of attention mentioned in Before Deployment during deployment;
2). Give up now;
3). Ask the community for help.
# Updates
- 2017-08-08 More troubleshooting guide
- 2017-08-06 Add troubleshooting guide
- 2018-02-09 Additional instructions
- 2018-04-05 Content Supplement
- 2018-09-03 Due to V2Ray updates, modify some descriptions
- 2018-11-09 Follow up the configuration format of the new v4.0+
- 2018-02-01 domainOverride changed to sniffing